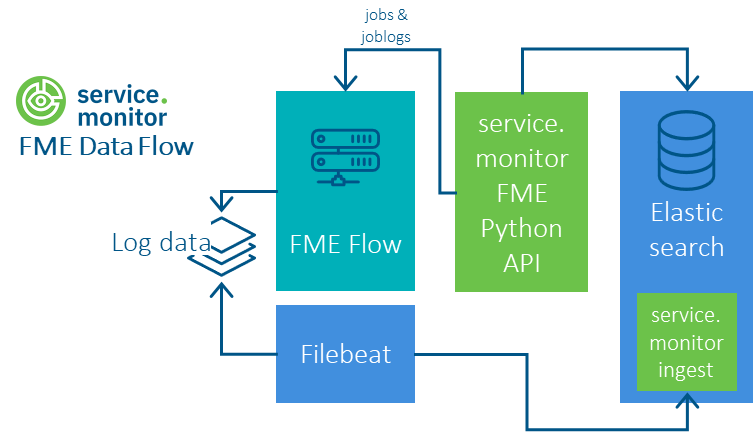
FME Flow
Procedure
-
Obtain FME Flow Token
-
Configuring of Python FME jobs
-
Configuring Filebeat for server only files
Obtain FME Flow Token
It makes sense to create a separate user account in FME Flow explicitly for the connection to service.monitor and to generate an FME token for this user. The following rights are required for access to FME when generating tokens in FME:
| Permission | Level |
|---|---|
Jobs |
Manage |
Licensing & Engines |
Manage |
Queue Control |
Manage |
Configuring of Python FME jobs
The Python API can be used to query FME flow jobs, job logs and the FME queues.
A Python 3 environment and the installation of pipelines-1.0.0-py3-none-any.whl are required for use. See README.md in the resources/analytics/python/pipelines folder.
The following steps should then be carried out:
-
Create configuration file config.json
-
Test the script on the command line
-
Embed script in executable file
-
configure continuous execution
The following JSON structure shows the configuration options for the FME Python Client.
Alternatively, the values can also be set as system environment variables. The names of the variables follow a schema derived from the path of the JSON structure, e.g. ELASTICSEARCH_URL.
{
"elasticsearch": {
"url": "http://elastic.host.example.com:9200",
"username": "elastic",
"password": "<elastic_pwd>",
"job_index": "ct-fme-jobs",
"log_index": "ct-fme-log",
"job_route_index": "ct-fme-jobroutes",
"hash_username": true,
"username_hash_salt": ""
},
"fme": {
"token": "<token>",
"url": "http://fme.host.example.com",
"pagesize": 1000,
"stage": "test"
},
"pipeline": {
"job_logs": {
"enabled": true,
"batch_size": 20
},
"common": {
"verify_ssl_certs": false
},
"proxy": {
"url": "http://proxy-host.example.com",
"use_forwarding_for_https": false
}
}
}
|
URL to Elastic |
ELASTICSEARCH_URL |
|---|---|---|
|
Name of Elastic user |
ELASTICSEARCH_USER |
|
password of the Elastic user |
ELASTICSEARCH_PASSWORD |
|
Activation of the hash function for the username |
ELASTICSEARCH_HASH_USERNAME |
|
Value that flows into the hash of the username |
ELASTICSEARCH_USERNAME_HASH_SALT |
|
URL to FME Flow |
FME_URL |
|
FME Flow Token |
FME_TOKEN |
|
Label for tagging events in terms of their stage |
FME_STAGE |
|
Activation of SSL certificate verification |
COMMON_VERIFY_SSL_CERT |
|
Once a proxy URL is specified, all traffic is routed through the proxy. |
PROXY_URL |
|
Whether requests should be forwarded to the HTTPS proxy or a TLS tunnel should be created using the HTTP CONNECT method. In standard scenarios, this option does not need to be changed. The forwarding can be used, for example, if the proxy used does not support the HTTP CONNECT method. |
PROXY_USE_FORWARDING_FOR_HTTPS |
python -m pipelines.fmejob -c /opt/conterra/fme/config.json#!/bin/sh
python -m pipelines.fmejob -c /opt/conterra/fme/config.json*/10 * * * * /home/monitor/fme-python/job-run.shConfiguring Filebeat for server only files
Filebeat must be installed on each FME host for which log files are to be collected.
The delivery of $service.monitor contains a Filebeat configuration in the directory \resources\analytics\elasticsearch\filebeat\fme-logfile, which
enables FME log files to be written to an Elasticsearch index using Filebeat. The data is transformed by a referenced ingest pipeline.
The configuration can be combined with other data sources, e.g. FME Flow. An example can be found in the directory \resources\analytics\elasticsearch\filebeat\arcgis-fme-logfile.
The variable fme.base.path can be used to define the base directory of the log data on the FME host once for all inputs.
|
The variable fme.env can be used to describe the environment that is integrated in terms of its stage: e.g. production or test.
|