Registering a new service
To create a new job for a service, register it via ![]() Service first.
Service first.
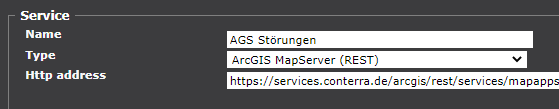
Specify the name, type and URL of the service.
-
The Name can be chosen freely. The name will be displayed in the list of monitored services on the management page where it can also be used for sorting and filtering.
-
The HTTP address contains the service URL without any added requests (e.g.
http://www.example.com/servletPath). -
The Type can be selected from a list:
| Esri related services | Safe FME | con terra & other services | OGC & INSPIRE |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
| The Type selection influences the available example requests and the way the server response is evaluated. |
How is a service monitored?
Each check of a service’s availability via a monitoring job is based on a request to the service and the subsequent verification of the response. The response is usually checked in the following order:
-
The HTTP endpoint is accessible (connection can be established)
-
Check of the HTTP status code (e.g.,
200 OK) -
Optional: Check of the response time (e.g., max. 2 seconds)
-
Check of the response content (e.g., for specific values or patterns, depending on the service type)
-
Optional: Additional user-defined checks via expectations