FME Flow
Procedure
-
Obtain FME Flow Token
-
Configuring of Python FME jobs
-
Configuring Filebeat for server only files
Obtain FME Flow Token
It makes sense to create a separate user account in FME Flow explicitly for the connection to service.monitor and to generate an FME token for this user. The following rights are required for access to FME when generating tokens in FME:
| Permission | Level |
|---|---|
Jobs |
Manage |
Queue Control |
Manage |
Configuring of Python FME jobs
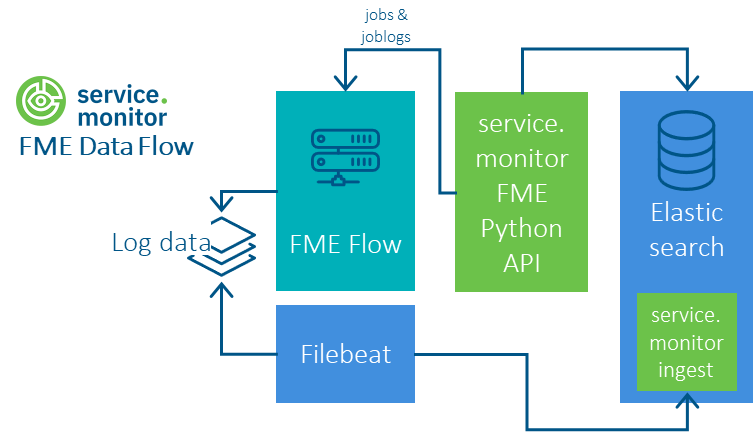
The Logstash pipelines from previous versions have been replaced by a Python API, which enables high-performance, reliable and easily configurable use. The FME flow jobs, the FME job logs and the FME queues can be queried in this way.
A Python 3 environment and the installation of pipelines-1.0.0-py3-none-any.whl are required for use. See README.md in the resources/analytics/python/pipelines folder.
The following steps should then be carried out:
-
Create configuration file config.json
-
Test the script on the command line
-
Embed script in executable file
-
configure continuous execution
{
"elasticsearch": {
"url": "http://elastic.host.company.com:9200",
"username": "elastic",
"password": "<elastic_pwd>",
"job_index": "ct-fme-jobs",
"log_index": "ct-fme-log",
"job_route_index": "ct-fme-jobroutes"
},
"fme": {
"token": "<token>",
"url": "http://fme.host.company.com",
"pagesize": 1000,
"stage": "test"
},
"pipeline": {
"job_logs": {
"enabled": true,
"batch_size": 20
}
}
}elasticsearch/url |
URL to Elastic |
|---|---|
elasticsearch/user |
Name of Elastic user |
elasticsearch/password |
password |
fme/url |
URL to FME Flow |
fme/token |
FME Flow Token |
fme/stage |
Label for tagging events in terms of their stage |
python -m pipelines.fmejob -c /opt/conterra/fme/config.json#!/bin/sh
python -m pipelines.fmejob -c /opt/conterra/fme/config.json*/10 * * * * /home/monitor/fme-python/job-run.shConfiguring Filebeat for server only files
The Filebeat component must be installed for each FME host that is to be involved in collecting the log data. Filebeat 7.x is currently supported; no problems have yet been identified with Filebeat 8.x.
The Filebeat configuration is then based on the template filebeat/fme-logfile/filebeat.yml.
# fme.base.path: '/var/log/fme'
fme.base.path: ''
# The value of this option will be added to the "labels.env" field in the index.
fme.env: 'production'
filebeat.inputs:
- type: "filestream"
id: "fme_server_core"
enabled: true
fields_under_root: true
fields:
labels:
env: ${fme.env}
source: "fme_server_core"
pipeline: "ct-monitor-fme-log"
paths:
- "${fme.base.path}/logs/core/current/*.log"
parsers:
- multiline:
type: "pattern"
pattern: '^(\w{3}-\d{2}-\w{3}-\d{4} \d{2}:\d{2}:\d{2}.\d{3})\s((AM|PM)+)'
negate: true
match: "after"
skip_newline: true
[... more inputs ...]
# ======================= Elasticsearch template setting =======================
setup.template.name: "ct-fme-log"
setup.template.pattern: "ct-fme-log-*"
setup.ilm:
enabled: true
policy_name: "ct-fme-log-policy"
overwrite: false
rollover_alias: "ct-fme-log"
pattern: "{now/d}-0000001"
# ================================== Outputs ===================================
# --------------------------- Elasticsearch Output -----------------------------
output.elasticsearch:
# The name of the target index
index: "ct-fme-log-*"
# The name of the ingest pipeline processing the filebeat input.
pipeline: "ct-monitor-fme-log"
# Elasticsearch host and port
hosts: ["https://localhost:9200"]
# Elasticsearch user name
username: ""
# Elasticsearch password
password: ""
ssl:
enabled: true
# Elasticsearch SSL fingerprint
ca_trusted_fingerprint: ""
The variable fme.base.path can be used to define the base directory of the log data on the FME host once for all inputs.
|
The variable fme.env can be used to describe the environment that is integrated in terms of its stage: e.g. production or test.
|
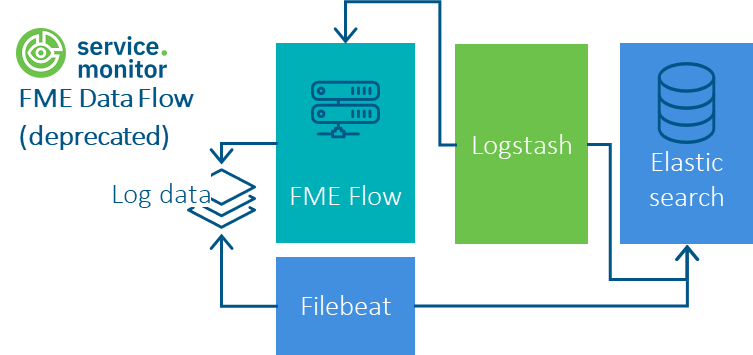
Setting up the Logstash Pipelines (deprecated, not mandatory anymore)
If all logstash pipeline folders of service.monitor are already present in Logstash, the three FME pipelines must be "activated" via the file pipelines.yml.
Configure pipeline
The FME pipelines must be configured by setting variables before they can be successfully commissioned.
| Variable | default | explanation |
|---|---|---|
FME_SERVER_BASE_URL |
<empty> |
URL of the host on which FME is running, incl. protocol, e.g.: |
FME_SERVER_TOKEN |
<empty> |
FME Flow Token for authentication of the request at FME |
FME_SERVER_LIMIT |
1000 |
Number of jobs to be queried per request at FME Flow |
FME_SERVER_SCHEDULE |
6h |
Polling interval for FME Flow jobs |
ES_HOST |
localhost |
Specify the address of Elasticsearch, e.g. |
ES_USER |
<empty> |
User name for authentication with Elasticsearch |
ES_PASSWORD |
<empty> |
Password for authentication with Elasticsearch |
Although retrieving FME jobs and joblogs via Logstash is deprecated now, this diagram provides you with a general overview.