Logstash Pipelines
Logstash comes with a customized configuration that meets the requirements of service.monitor.
This includes multiple data pipelines, schema templates for Elasticsearch, and the central configuration file pipelines.yml.
When Logstash is delivered, the file is not available and by using the supplied pipelines.yml you can use Logstash with multiple pipelines.
Typical file locations are:
| File or folder | Linux | Windows |
|---|---|---|
pipelines.yml |
|
|
ct-arcgis |
|
|
ct-[n] |
|
|
The files of the deployment need to be copied into the directories mentioned above depending on the operating system and installation type.
Depending on requirements, individual folders can be skipped if the data source is not to be included.
Afterwards the file pipelines.yml must be edited.
The variable PIPELINES_PATH must be set in a system variable.
- pipeline.id: ct-analytics
path.config: "${PIPELINES_PATH:/etc/logstash/conf.d}/ct-analytics/*.conf"
- pipeline.id: ct-fme
path.config: "${PIPELINES_PATH:/etc/logstash/conf.d}/ct-fme-jobs/*.conf"
- pipeline.id: ct-fme-log
path.config: "${PIPELINES_PATH:/etc/logstash/conf.d}/ct-fme-log/*.conf"
- pipeline.id: ct-fme-jobroutes
path.config: "${PIPELINES_PATH:/etc/logstash/conf.d}/ct-fme-jobroutes/*.conf"
- pipeline.id: ct-log
path.config: "${PIPELINES_PATH:/etc/logstash/conf.d}/ct-log/*.conf"
- pipeline.id: ct-monitoring
path.config: "${PIPELINES_PATH:/etc/logstash/conf.d}/ct-monitoring/*.conf"
- pipeline.id: ct-arcgis-logfile
path.config: "${PIPELINES_PATH:/etc/logstash/conf.d}/ct-arcgis-logfile/*.conf"If e.g. the pipelines ct-log, ct-arcgis-logfile and ct-monitoring should be operated, then all other pipelines must be removed from the file or commented out by #.
| Logstash uses one TCP/UDP port (e.g. 12201, 12202, 12203) per data pipeline when using service.monitor. Please check if access to this port from outside (depending on the purpose of use) is allowed by your firewall! |
Use of variables
Normally, no content changes need to be made in the files of the logstash pipelines, as these can dynamically resolve to system variables.
Different options are available for this
-
pass all system-specific values into system variables before starting the logstash process.
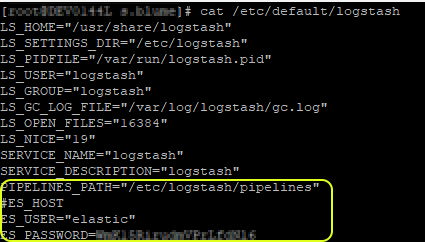 Setting Logstash Pipeline variables via /etc/default/logstash
Setting Logstash Pipeline variables via /etc/default/logstashThe recommended way to set variables is configuring these in
/etc/default/logstash. Another example for setting these values beforehand can be found in the filesbin/logstash_env.batandbin/logstash_env.sh. -
Windows users can also set these values via Set NSSM.
Variables overview
| Variable | default | explanation |
|---|---|---|
PIPELINES_PATH |
/etc/logstash/conf.d |
Specify the file system folder in which service.monitor’s logstash pipelines are located. |
ES_HOST |
localhost |
Specify the address of Elasticsearch, e.g. |
ES_USER |
<empty> |
User name for authentication with Elasticsearch |
ES_PASSWORD |
<empty> |
Password for authentication with Elasticsearch |
CA_CERT_PATH |
<leer> |
Absolute path to a |
FME_SERVER_BASE_URL |
<empty> |
URL of the host on which FME is running, incl. protocol, e.g.: |
FME_SERVER_TOKEN |
<empty> |
FME Flow Token for authentication of the request at FME |
FME_SERVER_LIMIT |
1000 |
Number of jobs to be queried per request at FME Flow |
FME_SERVER_SCHEDULE |
6h |
Polling interval for FME Flow jobs |
|
The specification of a valid path for In case of an HTTPS connection, use the |