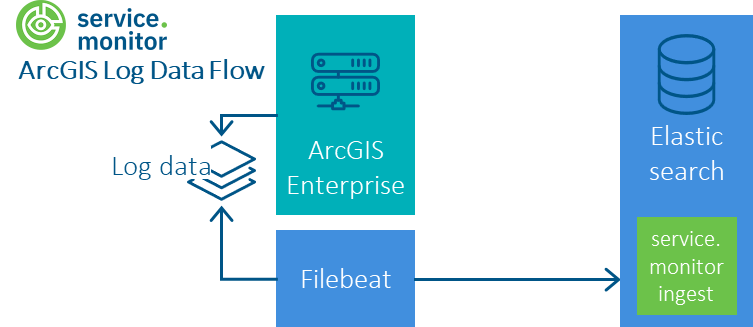
ArcGIS Enterprise Logdaten
Ablauf
Konfiguration von Filebeat mit Elasticsearch als Output
Die Auslieferung von service.monitor enthält im Verzeichnis \resources\analytics\elasticsearch\filebeat\arcgis-logfile eine Filebeat Konfiguration, mit
der ArcGIS-Logdateien mittels Filebeat in einen Elasticsearch-Index geschrieben werden können. Die Daten werden durch eine referenzierte Ingest-Pipeline transformiert.
Die Konfiguration kann mit weiteren Datenquellen z.B. FME Flow kombiniert werden. Ein Beispiel befindet sich im Verzeichnis \resources\analytics\elasticsearch\filebeat\arcgis-fme-logfile.