Optimize app startup
Performance Measurement
Any app managed with the map.apps Manager can be configured to collect performance data.
To enable the collecting of statistics the property enableStatistics has to be added to properties section of the app.json.
It is also possible to enable it for map.apps applications by configuring the option client.config.statistics.enabled in the application.properties.
| Name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Enables collecting of performance data for every app. |
To access the collected data the bundle apprt-statistics has to be added to an application.
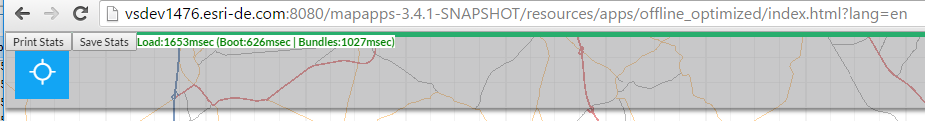
The apprt-statistics bundle adds two buttons and a startup time output to your app.
Print Stats opens a text input with detailed CSV structured data of the measured data.
Save Stats saves the detailed CSV structured data as a txt file into the application, this is only possible if you have previously logged in to the map.apps manager.
To interpret the CSV structure a developer requires deeper knowledge about map.apps.
Very important are the rows BundleController#_startBundle, which list the time a bundle requires to be activated.
This helps to find hot spots.
For a first impression the green text shows the time spent until the internal event FRAMEWORK_STARTED is fired.
It is separated into a boot and bundles section.
The boot section is the time required to prefetch all JavaScript data (if enabled) and to initialize the system bundle.
The bundles part is the time required to activate all bundles.
This time does not cover the time until the map is shown.
Important configuration options
| Name | Recommended Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
This activates the pre-fetching of the JavaScript files. This reduces the amount of requests to the backend system by fetching a lot of JavaScript files inside a single server request. These generated files are called "layer" files. To check if this flag is enabled check that two "resources/jsregistry/root/layer.js?mids=…." requests are executed. An indicator that something is wrong is if a lot of JavaScript files are loaded separately, especially if these are "<bundlename>/module.js" files. |
|
|
Adds "Expires" HTTP Headers to the files delivered by map.apps. This means that a browser is allowed to cache the files fetched from map.apps. The default value of 0.5 means that the browser caches the files for half a day. A value of |
|
|
This enables the file cache of the jsregistry. If this is not enabled, every layer file is regenerated with every access which can take long. If enabled, the generated files are reused. |
|
|
Defines the time files in the cache are valid. This can be set to -1 (unlimited) because map.apps tracks a bundle modification state and detects if a file is not longer valid, for example in case a bundle is updated. |
|
|
Defines the interval the class path scanner of the jsregistry detects bundles. Due to the fact that normally the classpath does not change it is sufficient that the scanner works only once at map.apps start. |
|
|
Defines the interval the directory scanner of the jsregistry detects bundles.
Set to |
Experimental: lazy startup (since 3.5.0)
It is possible to define that some bundles are started after all other bundles or after the event FRAMEWORK STARTED.
This is possible by adding a "lazy" attribute to the load section of the app.json.
"load": {
"allowedBundles": [
"system",
"splashscreen",
"map",
"..",
"measurement",
"editing",
"templates",
"templateslayout",
"templateslayout-dijit"
],
"lazy" : ["measurement", "editing"]
}Lazy bundles also have to be declared in the allowedBundles list.
The lazy state is ignored if any other bundle requires a lazy bundle.
Experimental: Start bundles by BundleTools
Another way to reduce the initial startup time is to define that some bundles are not started initially. These bundles can be started later by clicking a dedicated tool.
This requires two steps:
-
define the bundles which are started by default
-
define bundle tools
To define which bundles are started directly use the start property in the load section of the app.json.
|
This feature is experimental. By using the "start" property in an app, no optional dependencies are loaded. To use the map.apps template mechanism, add |
"load": {
// defines that the javascript of all allowedBundles is initally prefetched, not only the start bundles
"preFetchAll" :true,
"allowedBundles": [
"system",
"splashscreen",
"map",
"..",
"measurement",
"editing"
],
"start" : ["system","splashscreen","map","templates","templateslayout","templateslayout-dijit"]
}To define a tool that starts other bundles, the bundle Bundle Tools can be used.
With this bundle a tool can be defined in the app.json like this:
"bundletools": {
"BundleActivationTool": [{
"bundles": [
"measurement",
"editing",
],
"id": "toggleBundles",
"title": "Start Bundles",
"iconClass": "icon-pencil"
}]
}Minimize usage of proxy
Avoid to use proxy.use.always, because it routes any HTTP request over the /proxy endpoint of map.apps.
This has impact on the performance for loading server resources, because it adds extra network latency.
If the proxy is needed configure the proxy.use.rules property to define exactly which domain needs to be routed over the proxy.
Developer Tips
The startup performance highly depends on the work an Activator or a Component is performing during initialization. To optimize startup performance, reduce the runtime of initialization methods.
- Activator.start
-
A bundle Activator is the only class allowed to block the startup by returning a
Promisein the start method. This feature should rarely be used but is required for some features, for example to enforce login state or to load configuration data, which are needed by other bundles. For all other situations, the start method should return as short as possible and never returnPromises. - Component.activate
-
The component runtime parses all component declarations during the start of a bundle. If all requirements of a component are fulfilled at parsing time the component is instantiated, which has a direct impact on the startup time. Like the
Activator.startmethod, the code in the activate or init methods should finish as fast as possible. A good pattern is to initialize the internal state of a component asynchronous so that the activate method is not blocked. - Reference Injection
-
A developer should be careful with the work performed in injection methods like
add<reference name>, remove<reference name>, set<reference name>, unset<reference name>. These methods are called by the component runtime during the start of a component to inject the declared references. These methods should also be fast. It is bad practice if injection changes trigger widget/dom changes directly. A good pattern is to react asynchronous inside these methods, for example queue the parameters and perform the changes some milliseconds later. - MapModel
onNodeStateChanged,onStructureChangedevents -
A very high impact on the mapping performance have these MapModel events. It is very critical if the node tree is very complex. Widgets which rebuild their UI based in these events should react asynchronous on these events.
An complex application should try to minimize the initial MapModel complexity, to optimize the startup time of the map bundle, for example by deferred registration of initial not visible operational layers.
When modifying the MapModel programmatically a developer must use the right event to notify about the changes.
If nodes have been added or removed from the model fireModelStructureChanged has to be fired.
This causes the re-initialization of the map and related components.
In case only properties of nodes are changed, for example enabled, the function fireModelNodeStateChanged has to be fired.
The latter one only changes widgets, which is way more efficient than rebuilding all related widgets.